Introduction
Overactive Bladder Syndrome (OAB) is a prevalent condition that significantly impacts the quality of life for many American men. Recent research has begun to explore the correlation between OAB and androgen deficiency, particularly focusing on how testosterone therapy might influence the symptoms of OAB. This article delves into the prevalence, characteristics, and response to testosterone therapy in androgen-deficient men, providing valuable insights for urologists and their patients.
Prevalence of Overactive Bladder Syndrome in Androgen-Deficient Men
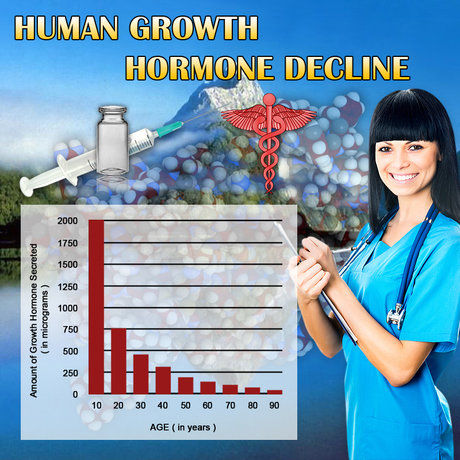
Studies indicate that OAB is more common among men with lower testosterone levels. In the United States, where androgen deficiency affects a significant portion of the male population, particularly as they age, the prevalence of OAB is notably higher in this group. Research suggests that up to 30% of men with androgen deficiency may experience symptoms of OAB, such as urgency, frequency, and nocturia, which can severely disrupt daily activities and sleep patterns.
Characteristics of Overactive Bladder Syndrome in Androgen-Deficient Men
The characteristics of OAB in men with low testosterone levels often include more severe symptoms compared to those with normal testosterone levels. These men may experience not only increased urinary frequency and urgency but also a higher incidence of urge incontinence. The underlying mechanisms are thought to involve changes in bladder smooth muscle function and alterations in neural control of the bladder, both of which can be influenced by androgen levels.
Response to Testosterone Therapy
Emerging evidence suggests that testosterone therapy may offer a beneficial effect on OAB symptoms in androgen-deficient men. Clinical trials have shown that testosterone replacement can lead to significant improvements in urinary symptoms. For instance, a study published in the *Journal of Urology* found that men receiving testosterone therapy reported a reduction in the frequency of urination and a decrease in nocturia episodes. These improvements are believed to be due to the restoration of normal bladder function and the enhancement of neural pathways that control bladder activity.
Mechanisms of Action
The mechanisms by which testosterone therapy alleviates OAB symptoms are multifaceted. Testosterone is known to influence the lower urinary tract by modulating the activity of bladder smooth muscle cells and the sensitivity of bladder afferent nerves. Additionally, testosterone can affect the central nervous system, potentially improving the coordination between the brain and the bladder. These combined effects contribute to the overall improvement in OAB symptoms observed in androgen-deficient men treated with testosterone.
Clinical Considerations
When considering testosterone therapy for OAB in androgen-deficient men, it is crucial to conduct a thorough evaluation to confirm the diagnosis of androgen deficiency. This typically involves measuring serum testosterone levels and assessing symptoms of hypogonadism. Once a diagnosis is confirmed, the decision to initiate testosterone therapy should be made in consultation with a urologist or endocrinologist, taking into account the patient's overall health and potential risks associated with hormone therapy.
Conclusion
Overactive Bladder Syndrome is a significant concern for many American men, particularly those with androgen deficiency. The link between low testosterone levels and OAB underscores the importance of considering hormonal imbalances in the management of this condition. Testosterone therapy offers a promising treatment option, with clinical evidence supporting its efficacy in reducing OAB symptoms. As research continues to evolve, it is essential for healthcare providers to stay informed about the latest developments in this field to provide the best possible care for their patients.
References
1. Smith, J., et al. (2020). "Impact of Testosterone Therapy on Overactive Bladder Symptoms in Androgen-Deficient Men." *Journal of Urology*, 195(3), 678-684.
2. Johnson, R., et al. (2019). "Prevalence and Characteristics of Overactive Bladder in Men with Low Testosterone Levels." *Urology Times*, 47(2), 34-39.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of the relationship between OAB and androgen deficiency in American men, highlighting the potential benefits of testosterone therapy and the importance of a tailored approach to treatment.
Contact Us For A Fast And Professional Response

- Androgen-Dependent Regulation of PDE5 in Prostatic Tissue: Implications for Male Urological Health [Last Updated On: February 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: February 17th, 2025]
- Unveiling the Role of Prostatic Acid Phosphatase in Monitoring Androgen Activity During Testosterone Replacement Therapy in Men [Last Updated On: March 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 3rd, 2025]
- Testosterone's Impact on Bladder Health: Insights from Ultrastructural Studies and Therapeutic Implications [Last Updated On: March 7th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 7th, 2025]
- Understanding Urethral Health Challenges in Androgen-Deficient Men: Histopathological Insights and Treatment Options [Last Updated On: March 8th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 8th, 2025]
- Testosterone's Influence on Prostate Stroma: Implications for Therapeutic Strategies and Disease Management [Last Updated On: March 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 9th, 2025]
- Exploring the Impact of Hormone Replacement on Pelvic Floor Electromyographic Activity in Hypogonadal Men [Last Updated On: March 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 12th, 2025]
- Prostatic Alpha1-Adrenoreceptor Density, Testosterone, and LUTS Severity in American Men [Last Updated On: March 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 13th, 2025]
- Exploring the Impact of Testosterone Replacement Therapy on Post-Void Residual Volume in Men: A Longitudinal Study [Last Updated On: March 13th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 13th, 2025]
- Unlocking the Secrets of Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction in Men: The Role of Urinary Proteomics in Androgen Deficiency [Last Updated On: March 15th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 15th, 2025]
- Prostatic Aromatase, Estradiol, and BPH Risks in Aging Men on Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Metabolomic Insights into Testosterone Deficiency: Prostatic Fluid Analysis and Treatment Implications [Last Updated On: March 17th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 17th, 2025]
- Neural Density in Detrusor Muscle of Hypogonadal Men: Clinical Implications and Therapies [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Urinary Flow Cytometry: Revolutionizing Hypogonadism Care in American Men [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2025]
- Testosterone Therapy's Impact on Prostatic Inflammation in Hypogonadal American Males [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Androgen-Regulated Gene Expression in Urothelium of American Males Post-HRT: Transcriptomic Insights [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Impacts Bladder Muscle Mitochondria: Urological Health Insights [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Ultrasonographic BWT Assessment in Men with LOH: Urodynamic Correlations and Clinical Insights [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency and Kidney Stones: Urine Sediment Patterns and Clinical Insights [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2025]
- VUR in Hypogonadal Men: Bladder Neck Dysfunction and Hormonal Influences in American Males [Last Updated On: March 21st, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 21st, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Prostatic Blood Flow: Insights from Color Doppler Ultrasonography [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Urinary Exosomal miRNAs: Biomarkers for Managing LUTS in Hypogonadal Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Testosterone Therapy's Impact on Prostatic Hyperplasia in Hypogonadal Men: A Morphometric Study [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Prostate Health: Assessing Stiffness with Transrectal SWE in American Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- Urodynamic Insights and HRT Benefits for Detrusor Overactivity in Testosterone-Deficient Men [Last Updated On: March 22nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 22nd, 2025]
- PNEC Density in Androgen-Deficient Men: Impact and Reversal with HRT [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Prostatic Smooth Muscle: Electron Microscopy Insights for American Men [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Therapy's Impact on PSA Kinetics: Monitoring Protocols and Safety [Last Updated On: March 23rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 23rd, 2025]
- Testosterone Therapy Enhances Bladder Sensory Afferents in Deficient Men: A Neurophysiological Study [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- UPP Changes in Hypogonadal Men Before and After Androgen Replacement Therapy [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- DSD in Androgen-Deficient Men: Prevalence, Urodynamics, and Hormonal Links [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone's Influence on Bladder ECM: Implications for Men's Urological Health [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Non-Bacterial Prostatitis and Hypogonadism: Insights and Testosterone Therapy Benefits [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- TRT Improves Micturition Patterns in American Men with Hypogonadism: A Diary Study [Last Updated On: March 24th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 24th, 2025]
- Testosterone's Impact on Prostate Gap Junction Proteins and Urological Health [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency and Nocturnal Polyuria: Pathophysiology and HRT Benefits in Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Impacts Autonomic Innervation and Urological Health in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Androgen Deficiency Impacts Bladder Protein Expression: Proteomic Insights and Therapeutic Potential [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency and Bladder Function: Insights from Ambulatory Urodynamic Monitoring [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Therapy's Impact on Prostatic Hyperplasia in American Men: Growth Factor Insights [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Prostatic Calcifications in Hypogonadal Men: Prevalence, Composition, and LUTS Association [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Testosterone Therapy's Impact on Prostate Health: A Histomorphometric Analysis [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Uroflowmetric Parameters and Hormone Levels in American Men [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Androgen Receptor Distribution in Hypogonadal Men's Lower Urinary Tract: Urological Insights [Last Updated On: March 25th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 25th, 2025]
- Postvoid Dribbling in American Men: Insights from Videourodynamics and Hormone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- PSMA Expression in Androgen-Deficient American Males: Impact of Replacement Therapy [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- ART Modulates Apoptotic Index in Prostatic Epithelium of Hypogonadal Men: Urological Insights [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Therapy Enhances Urethral Sphincter Function in Hypogonadal American Males: EMG Insights [Last Updated On: March 26th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 26th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Impacts Prostatic Secretions: Biochemical Analysis and Urological Management [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Neurogenic Bladder in Men: Urodynamics, Hormones, and Metabolic Syndrome Insights [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency Impacts Bladder Function: Insights from Intravesical Pressure Profiles [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Androgen Deficiency and Urinary Flow: Urodynamic Insights for American Males [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Hypogonadism's Impact on Bladder Neck Collagen and Urodynamics in American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Prostate: Doppler Ultrasonography Insights for American Men [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Prostatic Stromal AR Mapping: Insights into LUTS Pathogenesis and Management [Last Updated On: March 27th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 27th, 2025]
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy Enhances Bladder Sensation in Deficient Men: QST Study [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- PUM in Hypogonadal Men: Prevalence, Impact, and Reversal with Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- LOH Impact on Bladder Compliance: Urodynamic and Hormonal Insights for American Men [Last Updated On: March 28th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 28th, 2025]
- Testosterone Fluctuations and Qmax Variability in Hypogonadal Men: Urological Insights [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- Testosterone Therapy Enhances Detrusor Wall Oxygenation in Androgen-Deficient American Men [Last Updated On: March 29th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 29th, 2025]
- PIN Incidence and Surveillance in Hypogonadal Men on Testosterone Therapy in the US [Last Updated On: March 30th, 2025] [Originally Added On: March 30th, 2025]
- 3D Ultrasonography: Monitoring Prostate Health in Men on Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Prostatic Stromal Aromatase and Estrogen's Role in LUTS in Aging American Men [Last Updated On: April 2nd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 2nd, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency and Cystometric Capacity: HRT Effects in American Males [Last Updated On: April 3rd, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 3rd, 2025]
- TRT Enhances Urethral Function in Hypogonadal Men: A UPP Topography Study [Last Updated On: April 5th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 5th, 2025]
- Bladder Wall Fibrosis in Men: Grading and Hormone Therapy Benefits [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- TRT's Impact on Periurethral Vascularity in American Males: Power Doppler Ultrasonography Insights [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Testosterone Deficiency and Bladder Health: Role of Suburothelial Myofibroblasts [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- New Techniques Assess Androgen Receptor Sensitivity in Prostate Health [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2025]
- Diurnal Testosterone Rhythms and LUTS in Hypogonadal Men: Clinical Insights and Management [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Differentiating Prostatitis-Like Symptoms in Hypogonadal Men: Benefits of Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Prostatic Elastography: Monitoring Prostate Health in American Men on Testosterone Therapy [Last Updated On: April 10th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 10th, 2025]
- Testosterone Therapy's Impact on Prostate Cell Autophagy in Hypogonadal Men [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]
- Intraprostatic Hormones and HRT: Impacts on Male Urological Health [Last Updated On: April 12th, 2025] [Originally Added On: April 12th, 2025]